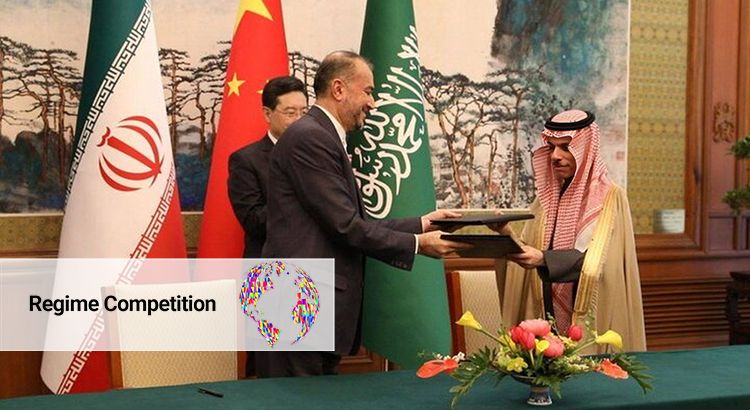
The Power of Not Using Power: China and the Saudi-Iranian Rapprochement
The intensifying systemic rivalry between great powers also involves contesting the most effective approaches to conflict resolution and mediation. The most recent Beijing-mediated détente between Saudi Arabia and Iran has ignited heated debates regarding its longevity and China’s rising profile in the region. While the Middle East may still be a region largely inhospitable to outsider mediation, there are three good reasons why Beijing’s latest foray into Middle East peace diplomacy may be effective. The article argues that China’s hitherto successful mediation between Saudi and Iran lies in its power of not using power—the ability to leverage its growing geoeconomic influence while refraining from the use of coercive power in regional affairs. This approach aims at providing an alternative approach to external powers’ engagement in Middle East peace affairs.