Schlagwort: China
The idea of publicly staged trials may appear grotesque or outdated to citizens of modern,...
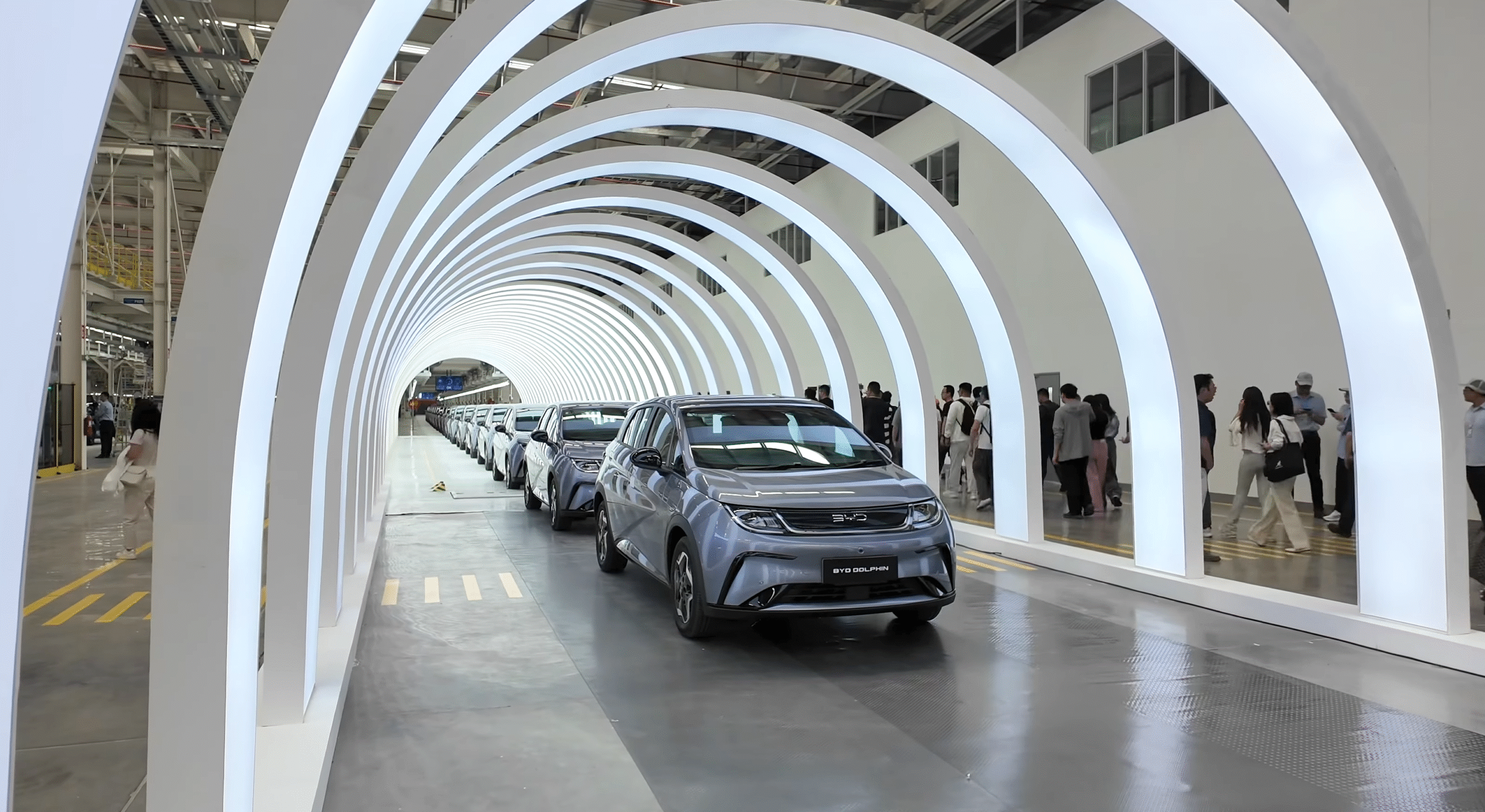
China’s Response to the EV Dispute: What it Tells us about the China–EU Rivalry
At first glance, Europe’s trade conflict over battery electric vehicles (BEVs) with China may...
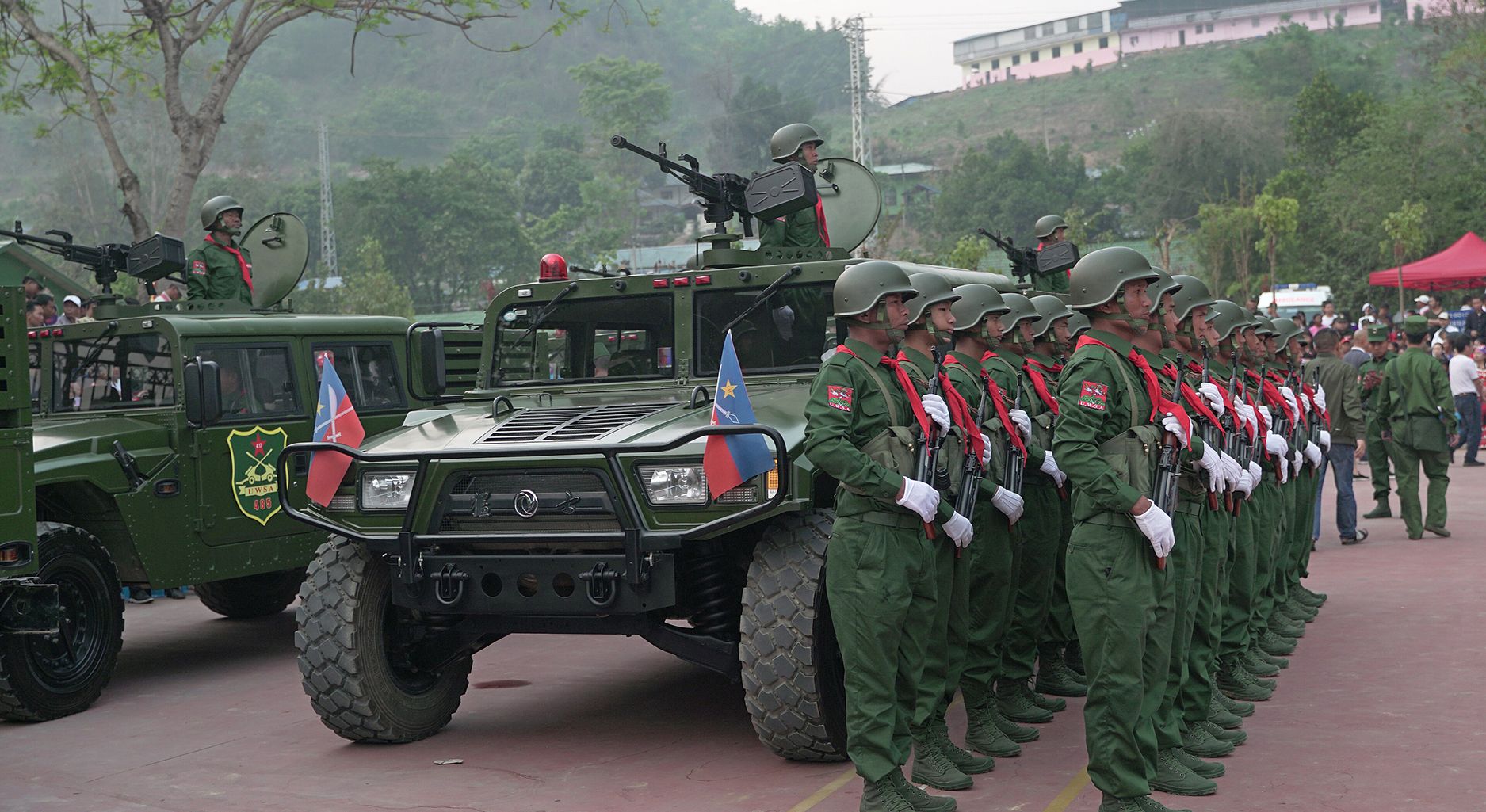
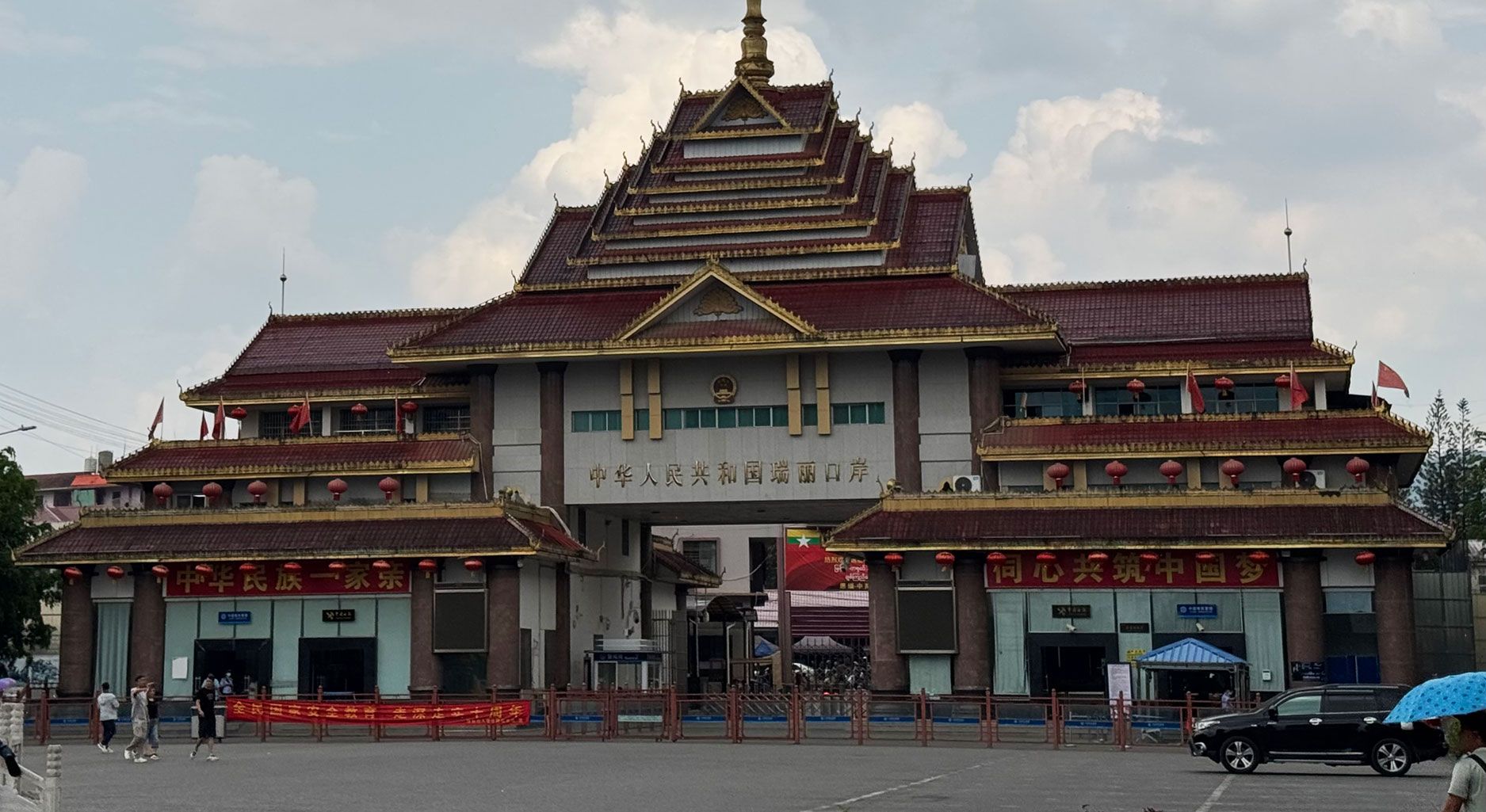
How Crisis Crosses Borders: Myanmar’s Civil War Shattered a Chinese Border Boomtown
Civil wars may not respect national boundaries. As civil war escalates in Myanmar, its...
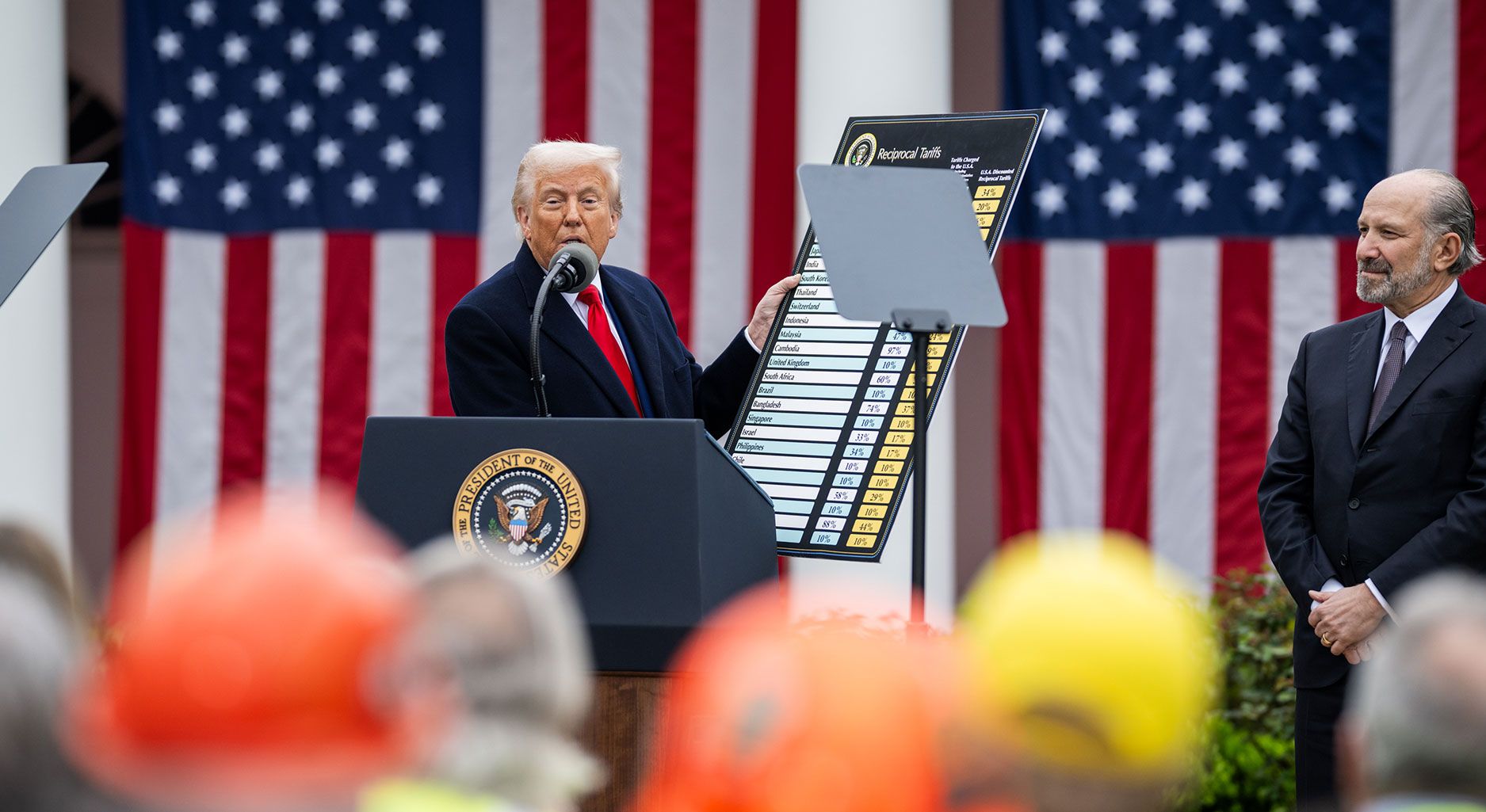
Es stehen nicht nur Exporte auf dem Spiel: der US-chinesische Handelskrieg und seine friedenspolitischen Konsequenzen
Am 3. April führte die Trump-Regierung im Rahmen ihres „Befreiungstags“ hohe neue Importzölle...
Maintaining the Rules-Based International Order: How Europe can Stand up to the Superpowers as an Alliance of Small States
When Western voices described the Russian invasion of Ukraine in February 2022 as an attack on...
Festhalten an der regelbasierten internationalen Ordnung: Wie Europa als Allianz kleiner Staaten gegenüber den Supermächten bestehen kann
Wenn westliche Stimmen den russischen Überfall auf die Ukraine im Februar 2022 als Angriff auf...
Confronting Antarctic Security. Let’s stop chasing spectres at the South Pole!
Antarctica is often celebrated as a continent of peace and science. All ‘measures of a military...
Germany’s Fragmented Approach to Disinformation in 2025 Elections
With elections taking place in less than a month, Germany finds itself faced with a critical...
Going over the Guardrails? China Policy in the 2024 US Election
No matter who wins the US presidential elections in November, the United States will likely...
With or Without you: Climate Policy After the US Elections
The potential re-election of Donald Trump would be a setback for the US climate policy of recent...