Schlagwort: Regimewettbewerb
Der russische Angriffskrieg auf die Ukraine und die seither ausgerufene „Zeitenwende“ haben die Debatte über Deutschlands zukünftige Außenpolitik erkennbar zugespitzt. Auch im Bundestagswahlkampf positionieren sich die Parteien zu schwierigen Fragen: Wie sollen Frieden und Sicherheit wiedergewonnen werden? Wie verändert sich die Weltordnung, und wie sollte Deutschland darauf reagieren? Dabei kommen sie zu teils sehr unterschiedlichen Antworten, die allerdings meist nicht über eine generelle Selbstverortung hinausgehen. Die chaotische Weltlage wird häufig als neuer „Systemkonflikt” zwischen Demokratien und Autokratien beschrieben, was jedoch die weitaus komplexere Realität nicht erfasst – und seit der Wiederwahl Donald Trumps auch keine praktisch umsetzbare Agenda mehr ist.
Do regime differences shape developmental engagement? How China and Japan compete in post-coup Myanmar
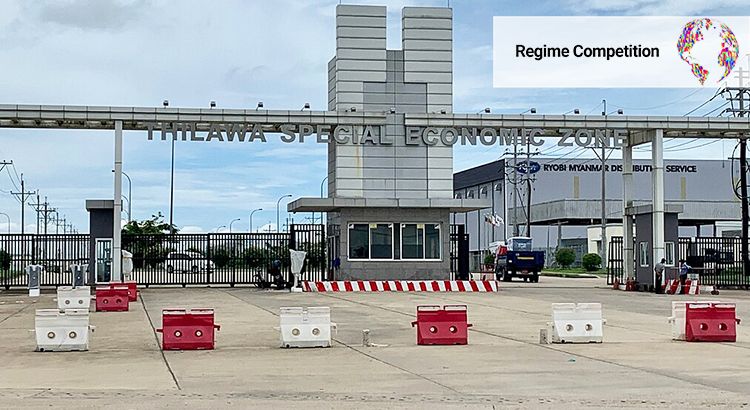
The 2021 military coup in Myanmar has left the country significantly isolated on the world stage. Politically, foreign governments have avoided recognizing the junta rulers, although quasi-official engagement is still underway. Economically, foreign investments into Myanmar have dropped by 42% from 2021 to 2022, off levels that had already massively decreased since the 2017 Rohingya expulsion. However, despite the international outcry over the new regime’s open warfare against civilians and the escalating violence in Myanmar’s multi-front civil war, both China and Japan have remained engaged in development cooperation, pursuing ambitious projects for economic corridors and special economic zones (SEZs) that were contracted under the deposed civilian government; in the case of China, even some new projects have been launched.
EU Democracy Support in the Southern Neighborhood: How the EU Contradicts its own Practices
For decades, the EU has declared that it aims to support democratization in its southern neighborhood. Yet, the EU’s cooperation with repressive rulers in other policy fields, such as energy, migration, security, and trade, contradicts the EU’s own democracy support objectives. European policymakers have apparently not learnt from the pre-2011 period. As we argue in our project SHAPEDEM-EU, the EU must embark on a journey of un-, de- and re-learning, and it must avoid contradicting practices in different policy fields. This can be done by introducing a democracy learning loop.
Debating Foreign Interference in a Multipolar World: Is the EU Becoming Illiberal?
The ways in which foreign interference by China, Russia and others are currently discussed in Brussels indicate that the EU is considering moving away from liberal principles in the area of international civil society support and the foreign funding of NGOs in particular. Based on a co-authored comment in the Heidelberg Journal of International Law, this blog post argues that it is helpful to read the current EU debate on foreign interference in the light of the ongoing, conflict-ridden transformation of the global order.
“Russian Self-Defense”? Fact-Checking Arguments on the Russo-Ukrainian War by John J. Mearsheimer and Others
In the ongoing Russo-Ukrainian war, and in the wider Russo-Western conflict, both sides compete over international influence as well as over how Ukraine and Russia are governed. While most would agree with this general assessment, prominent scholars like John J. Mearsheimer and others have argued that the West caused these confrontations by aggressively expanding its influence and preferred regime type into Ukraine, thus forcing Russia’s hand. However, while Russia’s perceptions of NATO evidently played a role in its decisions, a recent study finds that Mearsheimer’s arguments are at best incomplete and at worst simply false.
Germany’s New China Strategy: A Defensive Shift
After a lengthy process of internal deliberation, the German government released its China strategy on July 13. The document signals a policy shift away from the business-focused approach taken by previous governments, and towards a “de-risking” of ties with China. It also reframes the relationship by stressing elements of competition and even rivalry, based on the perception that Chinese authoritarianism is becoming a threat to Germany and its role in the world. Instead of seeking to transform autocracies through engagement, the new approach is much more about shoring up Germany’s own system.
Nicht darüber reden ist auch keine Lösung: Die Rolle von Autokratie und Demokratie in der Nationalen Sicherheitsstrategie
Mit dem Beginn des russischen Angriffskriegs auf die Ukraine wurde das Narrativ eines globalen Wettstreits zwischen Demokratien und Autokratien wiederbelebt, das bereits im Zuge des Aufstiegs Chinas an Bedeutung gewonnen hatte. Im März 2022 hatte auch Außenministerin Annalena Baerbock noch von einem „Bündnis von liberalen Demokratien weltweit“ gesprochen, das es gegen die Diktaturen dieser Welt zu schließen gelte. Etwas mehr als ein Jahr später hat die Bundesregierung nun ihre Nationale Sicherheitsstrategie veröffentlicht, in der vom Zwei-Lager-Denken nichts mehr zu finden ist. Diese positive Entwicklung wird jedoch konterkariert von einem weitgehenden Schweigen zu Fragen von Stabilität und Sicherheit, die sich im Umgang mit unterschiedlichen Regimetypen stellen – was auch keine Lösung ist, wie wir im Folgenden argumentieren.
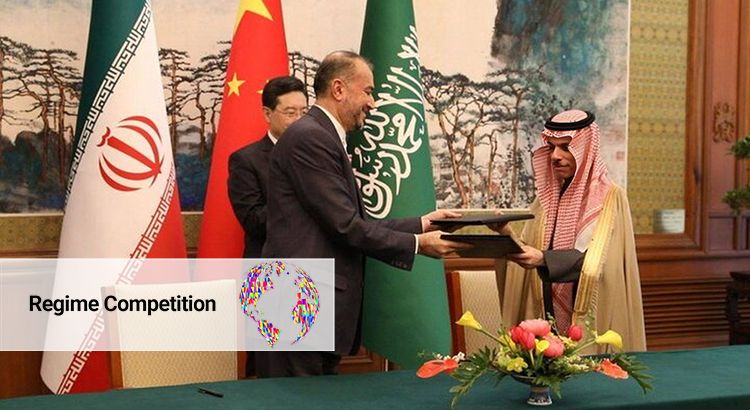
The Power of Not Using Power: China and the Saudi-Iranian Rapprochement
The intensifying systemic rivalry between great powers also involves contesting the most effective approaches to conflict resolution and mediation. The most recent Beijing-mediated détente between Saudi Arabia and Iran has ignited heated debates regarding its longevity and China’s rising profile in the region. While the Middle East may still be a region largely inhospitable to outsider mediation, there are three good reasons why Beijing’s latest foray into Middle East peace diplomacy may be effective. The article argues that China’s hitherto successful mediation between Saudi and Iran lies in its power of not using power—the ability to leverage its growing geoeconomic influence while refraining from the use of coercive power in regional affairs. This approach aims at providing an alternative approach to external powers’ engagement in Middle East peace affairs.
Is Antarctica Still Exceptional? The Case for “Co-opetition” at the South Pole
Antarctic diplomacy has famously shielded the continent of peace, science, and environmental protection from outside conflict and war. This “exceptionalism” is now being tested by Russia’s war against Ukraine and the belief that international strategic competition between great powers is spilling over into the Antarctic. In order to keep the Antarctic exceptional, however, it would be wise to refocus on what has made Antarctic diplomacy so successful in the first place: cooperation in order to compete, or “co-opetition.”
Decoupling and the “New Cold War”: Cautionary Lessons from the Past
An emerging “new Cold War” appears to pit democracies, led by the US, against autocracies, led by Russia and China. But the analogy between today’s regime competition and that of the “old” Cold War is deceptive. China and Russia today are much more closely intertwined with Western democracies than the Soviet Union ever was. These linkages will complicate the conflict considerably. There is already growing pressure to engage in “decoupling”, that is, to break these interdependencies. Research on past instances of decoupling shows that such processes often exacerbate conflict. This research offers four lessons about the general dynamics of decoupling – and little cause for optimism about today’s disengagement processes.