Um das Thema Chemiewaffeneinsätze in Syrien ist es im letzten Jahr in den Medien ruhiger geworden. In Den Haag, dem Sitz der Organisation für das Verbot chemischer Waffen (OVCW), gab es dagegen hitzige Auseinandersetzungen um die Einrichtung eines Investigationsteams, das die Verantwortlichen für solche Einsätze identifizieren soll und eigentlich die internationale Chemiewaffenkontrolle stärkt. Allerdings verschärften sich darüber die ohnehin tiefen Spannungen zwischen den Befürwortern und Kritikern der Entscheidung – mit potenziell negativen Auswirkungen auf die Arbeit der OVCW. Im April hat das neue Investigationsteam nun seinen ersten Bericht vorgelegt.
Kategorie: Serien/Reihen
Social Media as a Mirror of External Circumstances: Insights into the Perception of a Radical Group
Radicalisation processes take place in a field of tension between the actor and the outside world. External reactions and circumstances can have a supportive but also a rather negative and escalating effect on the dynamics of group development, depending on how they are perceived. Radical groups often react to circumstances in the outside world, incorporate them into their own discourse and provide their followers with a processed interpretation of them. This can be observed particularly well on social media. Within the scope of a thematic content analysis, we analysed how external circumstances were received within the community and what influence they had on the dynamics of the group Millatu Ibrahim.
The Great Divide? The Online-Offline Nexus and Insights from Research on the Far-Right in Germany
Research financed in the framework of the BMBF’s public security programme is still predominantly occupied with two issues: “online-radicalization” and “international terrorism”. The emphasis on „international terrorism“ still leads to an exclusive focus on “Islamist terrorism” and completely ignores the discussion of and a stronger need for research on right-wing terrorism. The emphasis on “online-radicalization” on the other hand misses the importance of also looking at the offline dimension of any phenomena under investigation.
Early Warning? Opportunities and Limitations of Automated Internet Monitoring
Policymakers have invested considerable effort and research funding to understand the role of the Internet in radicalisation processes and attack planning. This includes approaches to identify radicalisation or “weak signals” for terrorist intentions in online behaviour. As a result, security authorities have become increasingly interested in approaches to computer science including Artificial Intelligence. Nevertheless, what results have research efforts thus far yielded? Can computer science prove useful? And what are the possibilities and limitations of automated tools?
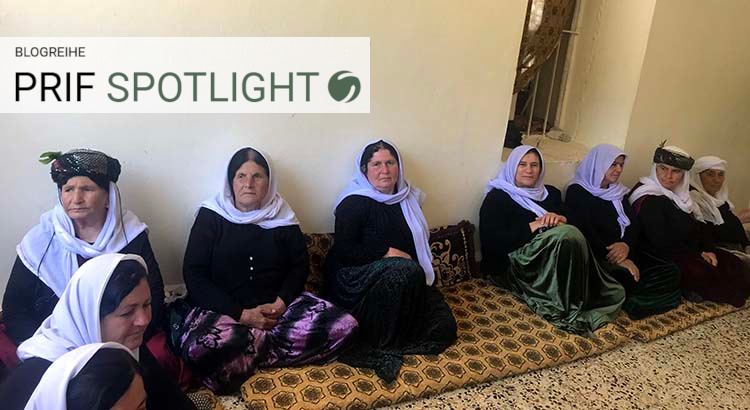

Endangered Future: Yezidis in Post-Genocide Iraq and the Need for International Support
As the international memory of ISIS’ genocide against the Yezidi population of Şengal in Northern Iraq recedes, its victims have been left to languish increasingly hopelessly, in refugee camps with little realistic prospect of returning to their homes. Tens of thousands of displaced Yezidis remain dispersed across Northern Iraq, hundreds of kidnapped Yezidi girls and women are unaccounted for and the fates of many of their male relatives unknown. In the short term, there is an urgent need for international protection from further attacks, the recognition of a political status for Şengal and immediate aid for refugee camps to create the conditions for Yezidi genocide survivors to return, resettle and gain a sense of political stability and empowerment.
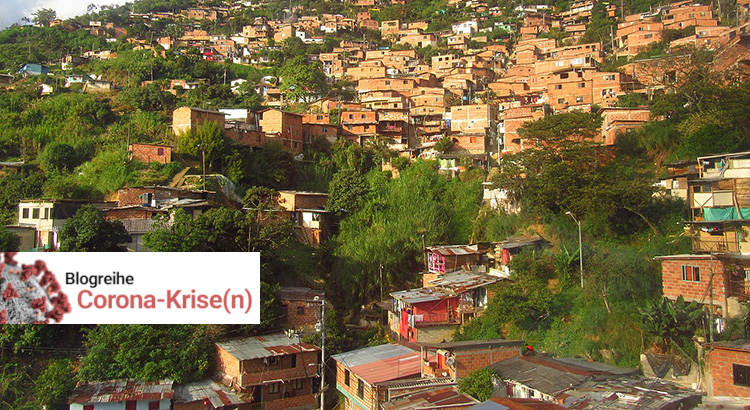

Se trata de estructuras, no de ayuda – Asentamientos informales y la desigualdad de la pandemia en Medellín, Colombia
En Colombia, el 25 de marzo se instaló una cuarentena nacional debido a la pandemia de la Corona. Pocos días antes, varias organizaciones no gubernamentales y comunitarias ya habían publicado una declaratoria con una alerta temprana a la alcaldía de Medellín – la segunda ciudad más grande de Colombia, premiada varias veces por su innovadora política urbana. En ese declaratoria, pidieron que se prestara especial atención a las personas que vivían en asentamientos informales y zonas periféricas: Las desigualdades existentes y las diversas formas de discriminación se exacerban debido a la creciente precarización de la informalidad a través de las medidas preventivas actuales. Los residentes de los barrios marginales se ven privados de los modos de sustento que han generado de forma independiente. Las intersecciones de las opresiones exponen a esas personas a riesgos mortales. Se necesita urgentemente un ingreso básico y protección de la salud.
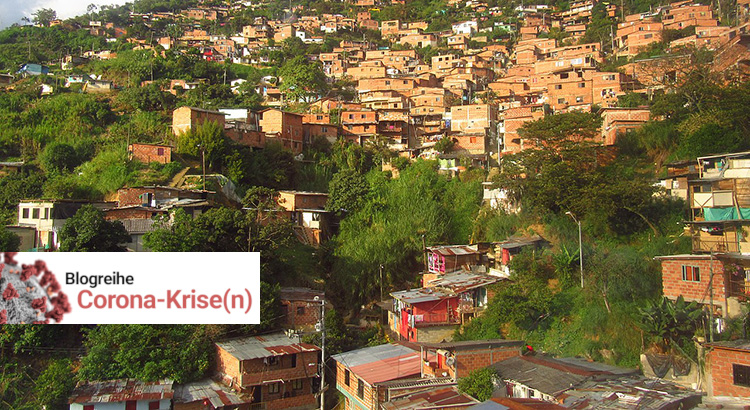

It is About Structures, Not Aid – Informal Settlements and the Inequality of the Pandemic in Medellín, Colombia
In Colombia, a national quarantine due to the Corona pandemic was installed on March 25th. A few days earlier, several non-governmental and community-based organizations had already published an alert statement in the city of Medellín – the second largest city of Colombia, awarded multiple times for its innovative urban policy. In this statement, they called for special attention to people living in informal settlements and peripheral areas: Existing inequalities and various forms of discrimination are exacerbated by the increasing precarisation of informality through current preventive measures. Residents of marginalized neighbourhoods get deprived of livelihoods that they have built up independently. The intersections of oppressions expose those people to deadly risks. A basic income and health protection are urgently needed.
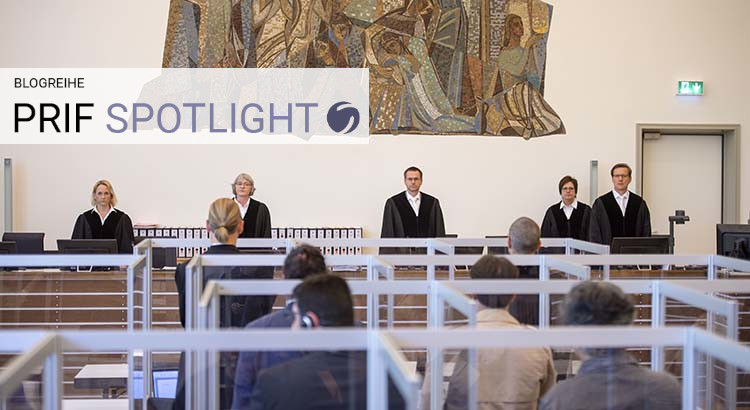

Syrische Folterer vor Gericht: Die partielle Rückkehr des universellen Rechts
Am 23. April 2020 begann in Koblenz ein Prozess, der weltweit Aufmerksamkeit auf sich zieht: Vor dem Oberlandesgericht müssen sich zwei Syrer verantworten, die an der systematischen Folter von Oppositionellen mitgewirkt haben sollen. Der Fall, über den in der Presse ausführlich berichtet wurde, fußt auf dem weltweit immer häufiger angewandten Weltrechtsprinzip. Welche Probleme die Anwendung des Prinzips mit sich bringt, wie berechtigt Kritik daran ist und wie das Koblenzer Verfahren vor diesem Hintergrund einzuordnen ist, beleuchtet dieses Spotlight.
Was die Covid-19-Pandemie mit Biowaffenkontrolle und Biosicherheit zu tun hat
Das neuartige Coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 ist keine Biowaffe. Es stammt höchstwahrscheinlich auch nicht aus einem Forschungslabor. Trotzdem wirft die Covid-19-Pandemie ein Schlaglicht auf bekannte und bisher ungelöste Probleme im Bereich der biologischen Abrüstung und Biosicherheit. Spekulationen über geheime Biowaffenprogramme werden durch die mangelnde Transparenz in zivilen und militärischen biologischen Forschungsprogrammen erleichtert. Und fehlende internationale Vereinbarungen zur Biosicherheit bedeuten ein geringeres Vertrauen in den sicheren Umgang mit denjenigen Forschungen, die zwar nützliche Ziele verfolgen, aber dabei selbst Risiken für Mensch und Umwelt bergen. Bisher bleiben die Vorwürfe, Covid-19 sei das Resultat eines Biowaffeneinsatzes, auf Einzelfälle beschränkt. Und dem Verdacht, es könne sich um einen Laborunfall gehandelt haben, stehen wissenschaftliche Studien entgegen, die einen natürlichen Krankheitsausbruch nahelegen. Trotzdem könnten solche Verdächtigungen in der ohnehin angespannten weltpolitischen Lage Krisen verschärfen. Wie ließe sich gegebenenfalls einer politischen Eskalation entgegenwirken? Welche Lehren lassen sich aus der Pandemie für die internationale Biowaffenkontrolle und Biosicherheit ziehen? Und welche Chancen ergeben sich vielleicht sogar aus dieser Krise?
Salafist Groups’ Use of Social Media and its Implications for Prevention
Researchers largely agree that radicalisation processes mostly include both real-world and virtual conditions. However, the interaction of both spheres has so far been understudied. Still, too little is known about how the two environments are mutually dependent and, accordingly, even less about how prevention and deradicalisation approaches can cover both spheres. In the previous article, Manjana Sold highlighted that while studying social media profiles, linkages to the real world are observable. This blog argues that this also occurs the other way around: Based on results from in-depth case studies, the article shows how radical Salafist groups in Germany use the benefits of social media to attract new members and facilitate the maintenance of the group. From these findings, possible starting points for prevention and deradicalisation work will be derived, which, if possible, cover both spheres of life.




